driven by clinical
EVIDENCE
Jobevne™ has achieved all the benchmarks for biosimilarity in efficacy and safety to the reference bevacizumab.1,2
Totality of evidence for JOBEVNE is based on similarity in analytical and clinical data, along with extrapolation of indications to Avastin®.1,2
EFFICACY
Study Design1
This Phase 3 study compared the efficacy and safety of JOBEVNE with Avastin, as first-line treatment for 671 patients with stage IV non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer.
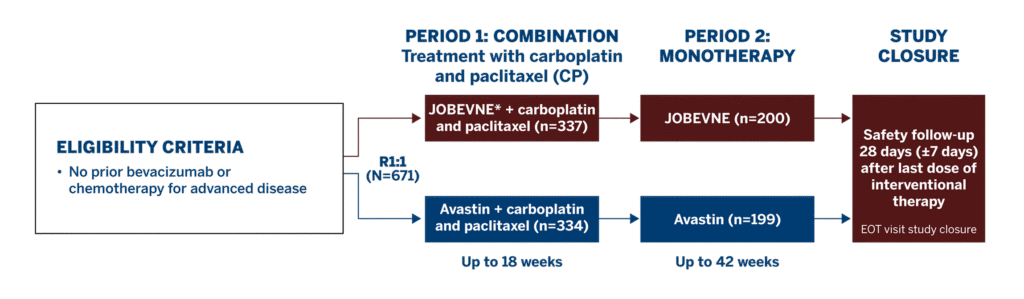
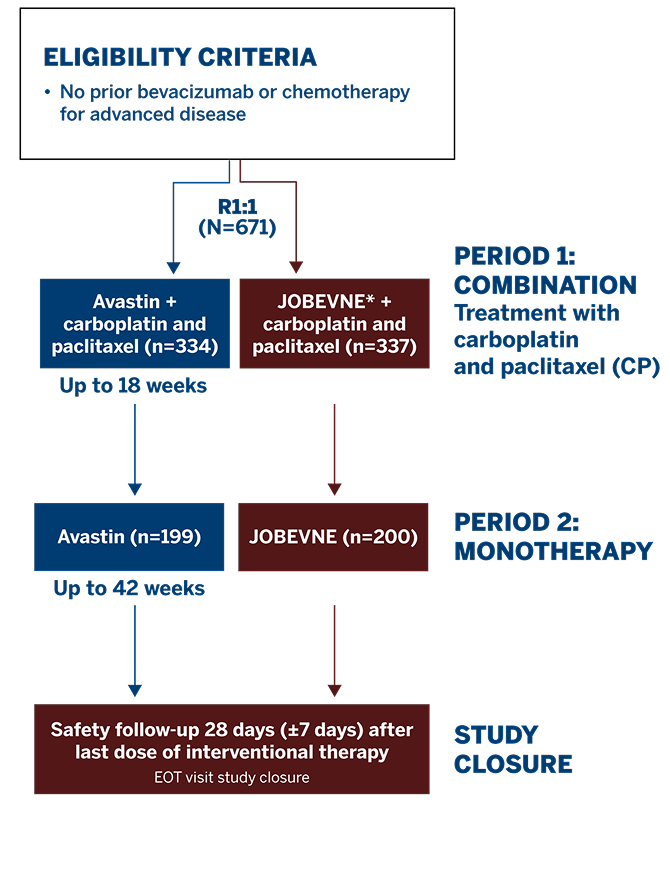
Study Endpoints1
-
- The primary efficacy endpoint was the overall response rate (ORR) at Week 18
- The key secondary efficacy endpoints were progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS)
- Immunogenicity testing was performed to detect anti-drug antibodies (ADAs) and neutralizing antibodies against JOBEVNE and Avastin
Baseline Characteristics1
-
- Demographics and baseline disease characteristics were well balanced between treatment groups with respect to age,† race, height, and ECOG status
*JOBEVNE was dosed at 15 mg/kg infusion.
†Eligible patients were adults ≥18 years of age.
ECOG=Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group; EOT=end of treatment; R=randomized.
ORR AT WEEK 181
- Primary endpoint: ORR was comparable between treatment groups at Week 18
- ORR ratio (0.96; 90% CI: 0.83, 1.12) and ORR difference (-1.6; 95% CI: -9.0, 5.9) were within their predefined equivalence margins*
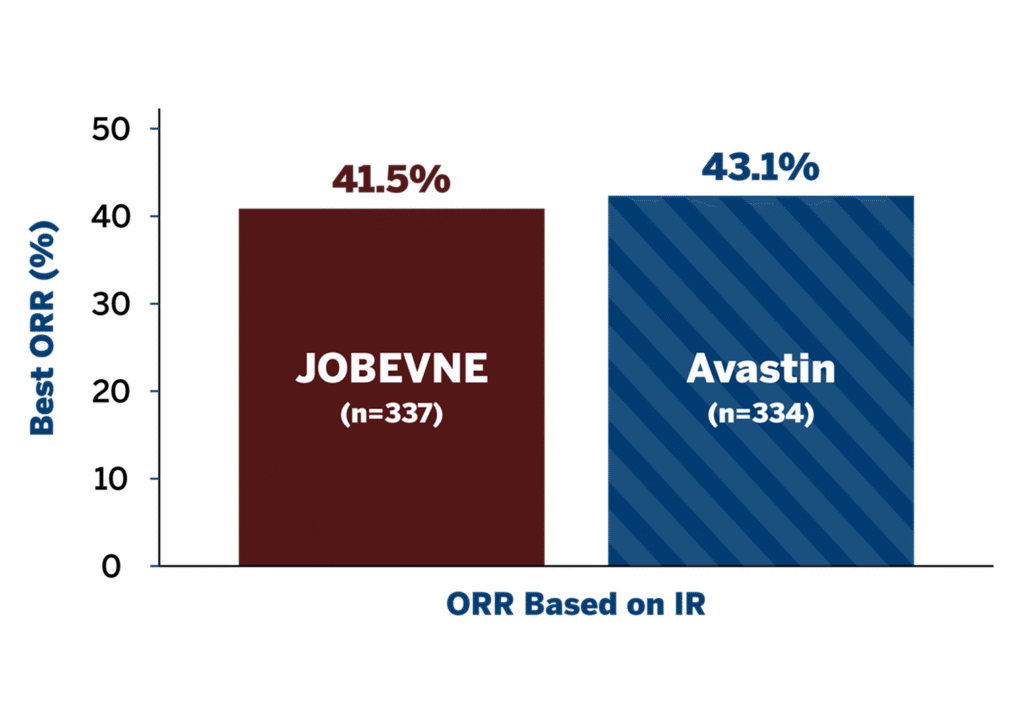
*ORR ratio 90% CI equivalence margin was defined as 0.73 to 1.36, and ORR difference 95% CI equivalence margin was defined as -12.5 to 12.5.
CI=confidence interval; IR=independent review; ORR=overall response rate.
PFS AND OS AT WEEK 421
There were no statistically significant differences in PFS at Week 42 between treatment groups.

*No statistically significant difference between treatment arms at 42 weeks; the log-rank test showed a P-value of 0.0906 (IR) between the treatment arms.
†The median OS was not reached in the ITT population at Week 42. According to the log-rank test, the difference between the survival curves for both treatment groups was not statistically significant (P=0.1185).
SAFETY
SAFETY AND IMMUNOGENICITY DATA DEMONSTRATE THE BIOSIMILARITY1
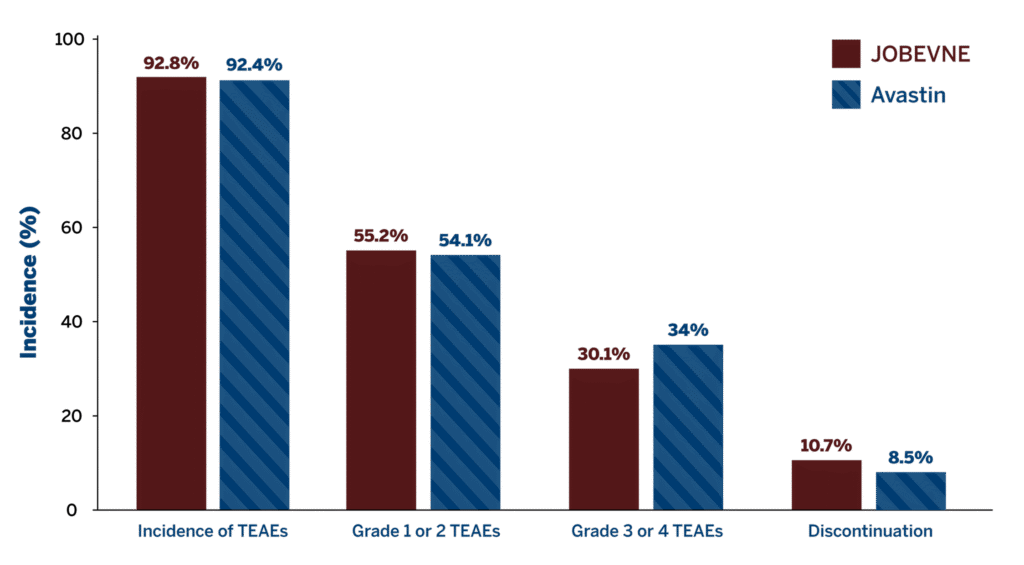
No clinically significant differences were observed between JOBEVNE and Avastin in the incidence of treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) and severity of immune responses.
Overall Incidence of Treatment-Emergent Adverse Events1
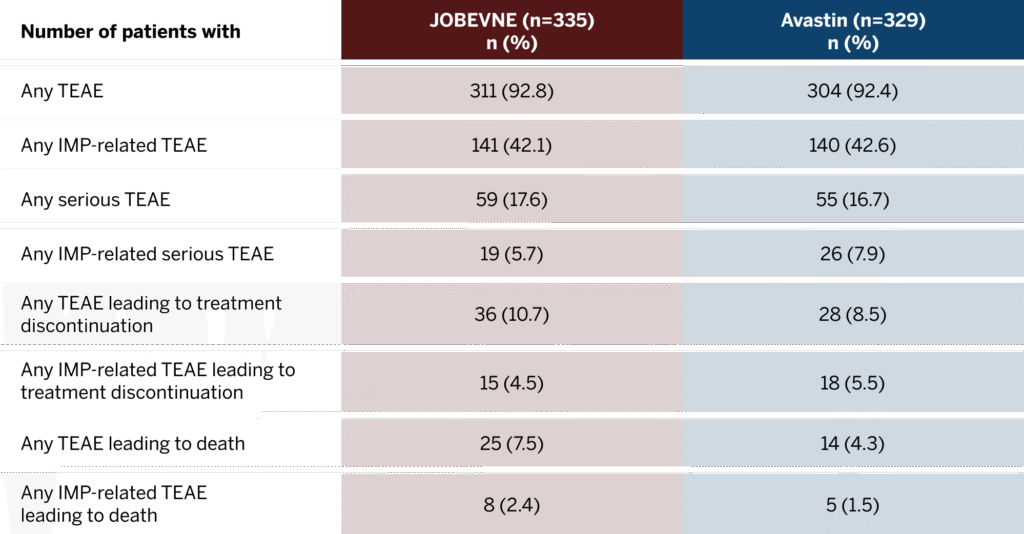
Includes Period 1 and Period 2 through Week 42.
Incidence of TEAE in treatment groups1
- Similar incidence of treatment-emergent ADAs compared with Avastin
- Similar incidence of neutralizing antibody post-baseline compared with Avastin
ADA=anti-drug antibody; IMP=investigational medicinal product; TEAE=treatment-emergent adverse event.
REFERENCES
1. Socinski MA, Waller CF, Idris T, et al. Phase III double-blind study comparing the efficacy and safety of proposed biosimilar MYL-1402O and reference bevacizumab in stage IV non-small-cell lung cancer. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2021;13:17588359211045845. 2. US Food and Drug Administration. Biosimilars: review and approval. Last updated December 13, 2022. Accessed June 16, 2025. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/biosimilars/review-and-approval
INDICATION AND Important safety information
INDICATION
Limitations of Use:
Fulphila is not indicated for the mobilization of peripheral blood progenitor cells for hematopoietic stem cell transplantationIMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
Do not administer Fulphila to patients with a history of serious allergic reactions, including anaphylaxis, to pegfilgrastim or filgrastim.
Splenic rupture, including fatal cases, can occur following the administration of pegfilgrastim products. Evaluate for an enlarged spleen or splenic rupture in patients who report left upper abdominal or shoulder pain after receiving Fulphila.
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) can occur in patients receiving pegfilgrastim products. Evaluate patients who develop fever and lung infiltrates or respiratory distress after receiving Fulphila for ARDS. Discontinue Fulphila in patients with ARDS.
Serious allergic reactions, including anaphylaxis, can occur in patients receiving pegfilgrastim products. The majority of reported events occurred upon initial exposure and can recur within days after discontinuation of initial anti-allergic treatment. Permanently discontinue Fulphila in patients with serious allergic reactions to any pegfilgrastim or filgrastim products.
Severe and sometimes fatal sickle cell crises can occur in patients with sickle cell disorders receiving pegfilgrastim products. Discontinue if sickle cell crisis occurs.
Glomerulonephritis has been reported in patients receiving pegfilgrastim products. The diagnoses were based upon azotemia, hematuria (microscopic and macroscopic), proteinuria, and renal biopsy. Generally, events of glomerulonephritis resolved after withdrawal of pegfilgrastim products. If glomerulonephritis is suspected, evaluate for cause. If causality is likely, consider dose-reduction or interruption of Fulphila.
White blood cell counts of 100 x 109/L or greater have been observed in patients receiving pegfilgrastim products. Monitoring of CBCs during therapy with Fulphila is recommended.
Thrombocytopenia has been reported in patients receiving pegfilgrastim. Monitor platelet counts.
Capillary leak syndrome has been reported after granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) administration, including pegfilgrastim products, and is characterized by hypotension, hypoalbuminemia, edema, and hemoconcentration. Episodes vary in frequency, severity and may be life-threatening if treatment is delayed. Patients who develop symptoms of capillary leak syndrome should be closely monitored and receive standard symptomatic treatment, which may include a need for intensive care.
The G-CSF receptor, through which pegfilgrastim and filgrastim products act, has been found on tumor cell lines. The possibility that pegfilgrastim products act as a growth factor for any tumor type, including myeloid malignancies and myelodysplasia, diseases for which pegfilgrastim products are not approved, cannot be excluded.
Myelodysplastic Syndrome (MDS) and Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) have been associated with the use of pegfilgrastim in conjunction with chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy in patients with breast and lung cancer. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of MDS/AML in these settings.
Aortitis has been reported in patients receiving pegfilgrastim products. It may occur as early as the first week after start of therapy. Manifestations may include generalized signs and symptoms such as fever, abdominal pain, malaise, back pain, and increased inflammatory markers (e.g., c-reactive protein and white blood cell count). Consider aortitis in patients who develop these signs and symptoms without known etiology and discontinue Fulphila if aortitis is suspected.
Increased hematopoietic activity of the bone marrow in response to growth factor therapy has been associated with transient positive bone imaging changes. This should be considered when interpreting bone imaging results.
The most common adverse reactions (≥ 5% difference in incidence) in placebo-controlled clinical trials are bone pain and pain in extremity.
You may report side effects to the FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Please see Full Prescribing Information.
